
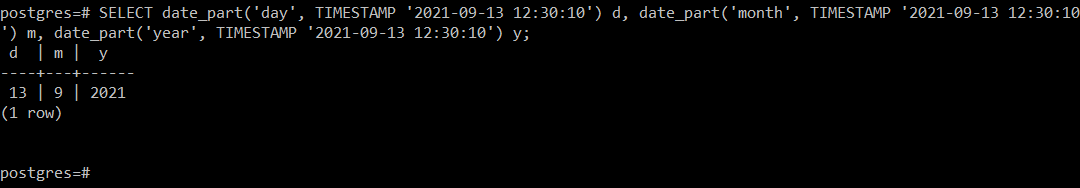
Unix time (which is also called epochs time) is kind of funky: it corresponds to the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1st, 1970. This function is usually used to format dates in specific ways as strings, so the arguments are the important part. FORMAT_DATE() – convert a date into a string.Sometimes you’ll need to specify what format the string is in through the function arguments. TO_DATE() – convert a string to a date format.TO_UNIXTIME() – convert a regular date format into a unix time date.FROM_UNIXTIME() – convert a unix time date into a normal date.Let’s go! Formattingĭates never seem to be in the format you want them to be in.Ĭomputers interpret dates in all different formats, from unixtime to strings and timestamps, and they’re usually not friendly to each other. In general, we’ll use “date” in this tutorial but the distinction isn’t super important. A TIMESTAMP is just a DATE with an additional two levels of precision: fractional seconds and fractional seconds with time zones. Something that often gets confusing is the difference between DATE and TIMESTAMP. Presto – a popular open source query engine built by Facebook and often used with HDFS / Hive.
Redshift – Amazon’s cloud based data warehouse (or at least one of them).BigQuery – Google’s cloud based data warehouse that shares SQL syntax with other GCP databases (Standard SQL).PostgreSQL – the world’s second most popular open source relational database, and a developer favorite for syntax.MySQL – the world’s most popular open source relational database (thanks, Oracle).We’ll tackle 5 broad categories:įor each function prototype, we’ll provide the right syntax and documentation for 5 of the more popular SQL dialects: When you’re working with dates, there are prototypes for types of functions: even though the exact syntax might differ between dialects, the idea is the same. Syntax is slightly different from MySQL to PostgreSQL (for example), and some dialects have functions that others don’t (e.g. Part of why writing SQL is annoying is that there are hundreds of different flavors.
Date object to postgresql timestamp for free#
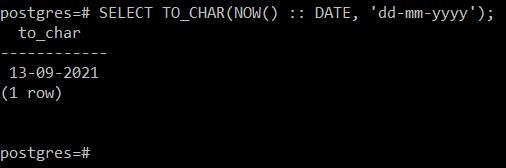
Get started for free 👉 SQL dialects and function prototypes Sidebar: With Retool you can build and internal tools remarkably fast using 50+ drag-and-drop components (including date and time pickers). This post will run through how you can effectively work with dates in SQL, resolve your issue quickly, and get back to bed. In Javascript you’ve got Moment, but parsing dates in SQL is a bit more complex. Nobody likes dates, especially programmers, but they’re a critical part of pretty much every application. It turns out migrating from Redshift to Bigquery was not “as easy as 123” and your DBA switched all of your timestamps to unix time. But slowly, your sweet dream turns into a nightmare: all of the queries you wrote earlier in the day are parsing dates wrong, your app is down, and your boss is angry. You can use DATE wherever you just need to keep track of the date and exact time is unnecessary while you can use timestamp where knowing the time is crucial.It’s 3AM, and you’re sleeping soundly in your room. ConclusionĭATE and timestamp have one main difference and that is that the DATE gives you only current date while timestamp gives you date in addition to the time ( with the option of time zones as well ). Both ‘timestamp’ and ‘timestamptz’ have min value of 4713 BC, a max value of 294276 AD, and a resolution of 1 microsecond/ 14 digits. If we talk about storage then both of these timestamp related data types would take 8 bytes each when they will be used. Whenever you need to know ‘timestamptz’ from database, PostgreSQL converts the UTC saved time back to the local time zone and displays it to you. Essentially, ‘timestamptz’ doesn’t give you time in UTC by default but rather PostgreSQL converts it for you and then save it in database. PostgreSQL will never save time directly in exact ‘timetamptz’ mode. Whenever you use this data type, PostgreSQL stores the values in table in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) format. The basic difference between both of them is that the former gives you time without time zone while latter gives you time with time zone. PostgreSQL provides two timestamp related datatypes ‘timestamp’ and ‘timestamptz’. The default format in both cases would be yyyy-mm-dd and if you want you can change that to any format you like.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
